Solving Banking Problems with the 5S Methodology – Part 2
The “5S Framework” is a methodology for solving banking problems that banks can apply to determine the best strategic path forward. We outlined the background and the first couple of steps of the framework in Part 1 (Here). In this article, we cover the remaining three “Ss” of “Solve,” “Stress,” and “Sell” while looking at some timely applications.
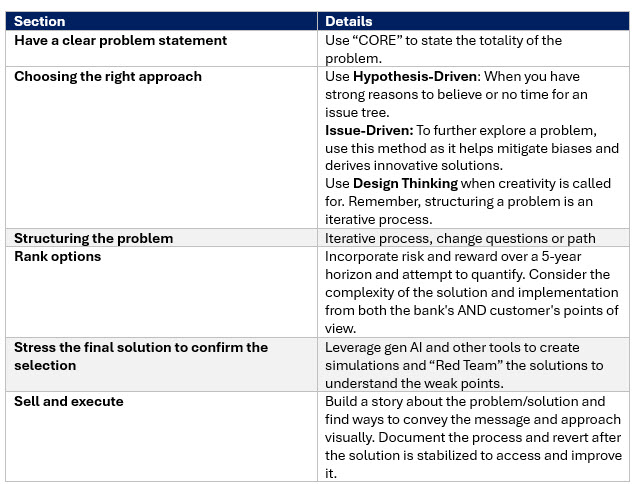
At last, we left it in Part I, we discussed how to choose the right problem-solving approach, whether hypothesis-driven, issue-driven, or applying Design Thinking to the challenge.
Step 3: Solve Analytically and Creatively
Once one of the three methodologies is chosen, you need to attempt to quantify the solution. One common deficiency at banks when deciding a solution is that they don’t specify a time horizon.
Let’s take an example. You apply the “CORE” method to define the problem of getting a better account opening platform. You go down the hypothesis-driven path and you determine you need new technology and so you define your requirements and jobs-to-be-done and you narrow down between a set of options. These options include using your core provider, Enable, Mantl, BankJoy, Terrafina Apiture, Alkami and others.
Your first step is to rank the cost of start-up and operations over five years using the same set of assumptions for each. You get the following table:
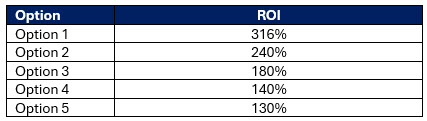
However, ROI is just one dimension. We can then take a more qualitative approach and include both the cost and the benefit, as well as non-financial items like the vendor’s cultural fit, the user interface, the ability to integrate with other platforms, and the design flexibility.
We then can rank them more subjectively.
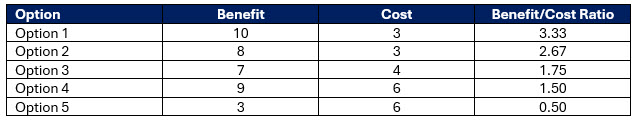
This second approach is also good for projects where you don’t have an ROI. It is OK to poll the group to build a consensus for non-objective criteria like culture.
With a general ranking, you can now test the top solutions.
Step 4: Stress the Solutions and Using AI
The next step is to decide how you want to stress. What we are looking at is the complexity of the solution or the variables around the option that might keep the bank from realizing the projected outcome and ROI. This can be done quantitatively by applying an expected value percentage that represents the volatility of the solution or the odds that it will not get completed as expected. This might look like the one below.
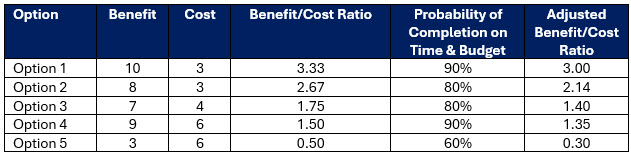
To leverage gen AI you can use a large language model to get very quantitative and produce a Monte Carlo model. Alternatively, to get more subjective you can have staff “Red Team” or critique the solution. To leverage gen AI, we outlined this approach Here.
The goal here is to understand the risk around the solution to better inform your decision before you settle on the best path forward.
Step 5: Sell and Executing the Solution
This step is all about selling or implementing the solution. The main thrust here is to present the solution to get approved. This step takes all the previous work and condenses it down to a single value proposition. Think of this step as creating a story about the solution tailored to those you are trying to convince, be it fellow managers, the board, or staff. This story should include the following:
- Describe the current situation and the challenge that exists for the bank.
- Describe the process and summary of the universe of options – how many were considered and what they represent in terms of all possible solutions available to the bank.
- What is the recommended option, and why does that make sense with regard to return, risk, and benefit?
- What are the next steps?
- How do you want to document the selection and decision process so that you can review it later for quality control and forecasting accuracy? This step is not to be overlooked. It is far too common for bankers not to revisit their decisions after a solution is implemented to validate their process. Understanding if the problem was defined accurately in retrospect, if enough solutions were reviewed, and if the solutions were diligent enough is critical for future improvement.
Using the 5S Framework For Solving Banking Problems
The 5s Framework isn’t the only problem-solving framework available to bankers but we have found it the most flexible and encompassing solution to handle solutioning strategic challenges within a regulated environment where decisions need to be methodically handled and documented. Following the 5S framework provides bankers a structure to make better decisions and be more confident in those decisions.
To recap:
Solving banking problems is like any other skill in that it is something to learn, practice, and train others on until it is a standard skill enterprise wide. The more bankers use this framework, the more efficient problem solving becomes, as bankers learn to better define the problem at the start and gather information about the solutions early.

